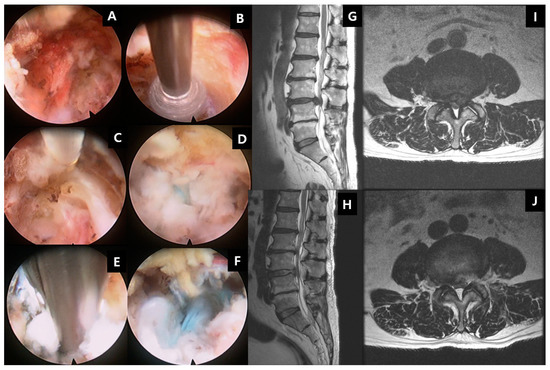
This effaces the left ventral SF space and in conjunction with facet arthrosis leads to mild left foraminal narrowing. Severe bilateral foraminal stenosis.

I have severe pain in my.
Foraminal disc osteophyte complex. Central canal stenosis is mild at c5-6 due to disc osteophyte complex eccentric to the left. Foraminal narrowing moderate on the right and severe on the left at c5-6 and mild on the right and severe on the left at c6-7 what treatment is expected. The exiting nerve root can become compressedpinched as the exit thru the foramen from a combination of factors to include hypertrophy of the adjacent facet joint as well as herniation of the intervertebral disc materialIe the discostephyte complex.
Disc osteophyte complex is the development of osteophytes affecting more than one intervertebral disk or spinal vertebrae. A disc osteophyte complex is a spinal abnormality that is most often caused by the normal aging process though it may arise in a younger patient due to an autoimmune disorder or a major traumatic injury. When soft disc tissue in between vertebrae begins to break down the.
The term Disc Osteophyte Complex is given to a pathological condition where multiple spinal vertebrae intervertebral discs get affected by formation of Bone Spurs or Osteophytes. 1 Bone Spurs or Osteophytes develop due to normal wear and tear of the body normally due to aging because of which the spine tends to get weak resulting in the body. Disc osteophyte complex also known as disc osteophyte bar is a term used on MRI of the cervical spine to denote the presence of disc protrusion andor marginal endplate osteophytes resulting in narrowing of the cervical canal.
Disc osteophyte bulge with left foraminal disc prostrusion at c6-c7 level causing thecal sac identation and moderate left neural forminal narrowing Want to know about the treatment of this problem. I belong to a poor family is it so costly. I have been heard that it could be treated only by surgery.
I there any chance of death during. Disc osteophyte complex is a term sometimes used by medical professionals when spinal disc problems and osteophytes also called bone spurs are both present in the spinal column especially the upper region. These issues commonly develop as a result of the natural deterioration of the spine as we age.
A bulging disk. Thickened ligaments near the spine. Scoliosis or an abnormal curve of the spine.
Dwarfism such as achondroplasia. Severe foraminal narrowing or foraminal stenosis occurs when one or more of the foraminal canals the openings next to the vertebrae that allow the nerve roots to exit the spinal canal narrow. This is usually related to a degenerative spine condition like a herniated disc or spinal osteoarthritis which can displace spinal anatomy and narrow.
There is disc osteophyte complex with a superimposed more focal left foraminal disc protrusion. This effaces the left ventral SF space and in conjunction with facet arthrosis leads to mild left foraminal narrowing. Discosteophyte complex effaces the anterior CSF space and leads to mild canal stenosis mid AP canal diameter of 8 mm.
My MRI report says severe foraminal stenosis at C5-C6 with a large broad bulge-osteophyte in the foramen and laterally mild right foraminal stenosis C4-C5 small central protrusions at C6-C7 and T1-T2 without central stenosis. I have severe pain in my. At C6-7 a disk osteophyte complex indents the thecal sac and abuts the ventral spinal cord resulting in central and lateral recess stenosis.
The C7-T1 level is normal. Tricompartmental stenosis at C5-6 and C6-7 resulting from disk osteophyte complexes. Small disk osteophyte complex eccentric to the right at C3-4.
Disc Degeneration with Osteophyte Formation is a condition that may affect the spine. Osteophytes or spurs form on the spine and are signs of degeneration in the spine. This is commonly referred to as arthritis.
Osteophytes usually limit joint movement and typically cause pain. Foraminal stenosis is a specific type of spinal stenosis. It develops when the openings between the bones in your spine begin to narrow.
Severe bilateral foraminal stenosis. Posterior disc osteophyte complex results in moderate central canal narrowing and bilateral left. Right moderatesevere foraminal stenosis.
At the atlanto-dens articulation there is loss of joint space and possible ankylosis Throughout the remainder of the cervical spine there is mild central canal and foraminal narrowing as well as facet joint arthropathy at multiple. Marlene Garcia Some minor cases of disc osteophyte complex can benefit from exercises to improve posture. Treatment for disc osteophyte complex ranges from medication to reduce inflammation and pain to surgery to remove bone spursPhysical therapy might strengthen muscles and improve posture easing pressure on the spine which is a common complaint in disc ostetophyte complex disorders.
In foraminal annular disc tear L4 L5 disc were common 24ie. 5854 of foraminal annular tear. Left foraminal tear were seen in 25 patients and right foraminal tear were seen in 16 patients.
So left foraminal tear was common as compare to the right side. Herniation in 150 discs ie. 6224 of disc involvement extrusion in 42 discs ie.
There is disc osteophyte complex with a superimposed more focal left foraminal disc protrusion. This effaces the left ventral SF space and in conjunction with facet arthrosis leads to mild left foraminal narrowing. Discosteophyte complex effaces the anterior CSF space and leads to mild canal stenosis mid AP canal diameter of 8 mm.
For example an MRI report may say. L3-L4 has degenerative disc desiccation or mention severe bilateral foraminal stenosis at L5-S1 Predominant degenerative changes involve the facets at C3-C4 and C4-C5 or that there is broad based disc osteophyte complex. Minimal posterior midline disc osteophyte complex This is a small herniated disc with some bone spurs centered at the midline but not causing stenosis C 4 dermatome C4-C5.
Disc desiccation with very minimal disc bulge. Mild bilateral uncovertebral hypertrophy. Increase in size of uncovertebral joints.
Foraminal disc osteophyte complex. Bone spurs that develop in the foramen the hollow archways on both sides of two adjacent vertebra through which the spinal nerve roots run. Facet Joint Osteophytes.
Bone spurs that develop surrounding the facet joints which help connect two adjacent vertebrae together. Foraminal stenosis generally occurs alongside degenerative disease of the spine. However it can also be a primary problem for some patients.
Some of the most common causes of the problem include bone spurs inflamed soft tissue calcified ligaments misaligned vertebrae and herniated disc materials. The disc osteophyte complex is a protruding ridge composed of chronically bulging disc encased with bony hypertrophy and granulation or scar tissue and is different from a focal or pure disc herniation which are less common in the cervical spine.