
The outer ring beyond the black outline represents a disc that is symmetrically bulging which is very rarely seen in CT or MRI scans. L5-S1 bulging discs are most common as they take the stress and weight of the body.
Your spine is made up of a column of bones stacked on top of each other.
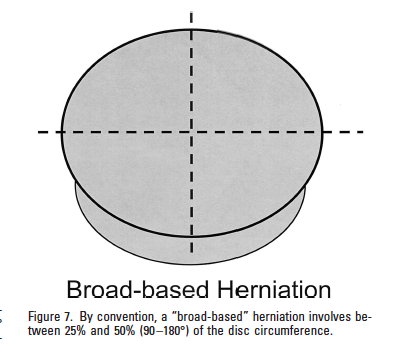
Broad based posterior disc bulge. A broad-based disc protrusion occurs when more than 25 percent but less than 50 percent of the disc materials circumference is extended beyond the spinal bone borders according to the American Journal of Neuroradiology. A disc is bulging when over 50 percent of the disc materials circumference is overextended. A disc has either a broad-based.
Broad based posterior disc bulge l4 l5 By. Robert Shepherd MS Certified Medical Illustrator Vice President and Director of Eastern Region Operations MediVisuals Incorporated It is difficult to appreciate the subtle differences between the various types or severities of intervertebral disc injuries that result in them being defined as bulges herniations protrusions extrusions. A posterior bulging disc or herniated disc occurs when a spinal disc beings to bulge.
A posterior bulging disc also known as a herniated disc occurs when a spinal disc that sits between vertebrae begins to bulge due to compression. This condition can be. What is a disc bulge.
It is a condition wherein a part of the disc extends beyond the normal limits and the internal part of the disc remains intact in the fibrous ring. The bulging is always broad thus the term broad based disc bulge. When the size of the herniation is 25 to 50 of the total disc circumference the disc pathology is described as being broad based.
When the degree of bulge is less than 25 the condition is described as being a focal herniated disc. Sometimes a broad based herniation is represented on a circular map in which case the herniated portion is 90 to 180 degrees of the total 360. A posterior disc protrusion is a disc that has bulged toward the posterior rear or away from the abdomen of its usual position.
The posterior side of the disc is adjacent to the spinal cord and nerve roots branching off the spinal cord. A posterior bulge therefore can. A bulging disc occurs when the nucleus pulposusthe soft jelly-like center of the disc that gives the disc shock-absorbing capacitiesextends beyond its normal position inside the disc structure but remains contained within the annulus fibrosus.
Broad based disc bulge is the issue of have no extra room for the persons spinal cord causing pain and numbness. Broad based disc bulge is often thought to. Bulge is a term for an image and can be a normal variant usually at L5-S1.
It can result from advanced disc degeneration or from vertebral body remodeling as consequent to osteoporosis trauma or adjacent structural deformity. It can also occur with ligamentous laxity in response to loading. Over time the discs in the spine undergo wear and tear due to repetitive movements.
This process is absolutely normal and is a part of aging and happens with everyone. L5-S1 bulging discs are most common as they take the stress and weight of the body. The symptoms experienced in the lower back can be terribly painful.
The causes of L4-L5 bulging disc. Its important to know the mechanics of your spinal column and what is happening during a disc bulge so you can embark on the proper treatment with your spine doctor. Your spine is made up of a column of bones stacked on top of each other.
Discs provide cushioning between each of these bones said Livestrong. Sometimes discs may bulge move out. Broad disc protrusion only produces symptoms like numbness tingling and pain when the disc compresses a nerve root or the spinal cord.
Some of the methods that doctors use to confirm a diagnosis of broad disc protrusion include. Medical history and physical. This involves an accurate description of the location and nature of symptoms to your physician.
Your physician will want to know about how. Posterior annular disc bulges with subtle tear. Prolapse L5-S1 L4-L5 noted at L4-L5 and L5-S1 with mild right paracentral and foraminal broad based protrusion indenting the ventral thecal sac causing bl lateral recess narrowing with abutment over bl traversing nerve roots.
Treatment for a disc bulge in L4-L5 includes physical therapy and waiting to see if symptoms abate on their own or a surgical repair. The majority of bulging discs occur in the lumbar or lower region of the spine. Non-surgical treatments can be used to alleviate the pain while the patient waits for symptoms to go away on their own.
Disc protrusions are asymmetrical disc bulges that usually affect one side of the disc with the possibility but not always of compressing nerve tissue. People often describe their pain as a pinched nerve but true symptoms of nerve compression are those of sensory changes such as pins and needles paraesthesia or numbness anaesthesia loss of strength and reduced reflexes. Here are the four stages of a disc herniation or disc bulge.
Think of the disc like a flat hard onion with strawberry jelly inside. The jelly is the nucleus while the onion layers form circular layers of hard cartilage called the annulus. A disc bulge is just what it sounds like.
A circumferential enlargement of the disc that is broad based in general. A disc herniation usually is either a protrusion or extrusion. A protrusion is one where the base the part that attaches to the disc is.
A bulging disc osteophytes or osteoarthritis can lead to impingement or something pressing on another structure. The terminology associated with this problem is thecal sac impingement or a herniated disc providing a mass effect compressing displacing or encroaching on. Specific Lumbar bulging discs can also result in weakness numbness and tingling in the legs as well as muscle spasms.
Bulging disc symptoms can worsen with coughing sneezing and bending. When a lumbar bulging disc exerts pressure on the sciatic nerve the resulting symptoms are commonly referred to as sciatica. Bulging disc is purely descriptive.
The term should not be used in a diagnostic term. The diagram shows a top down view of a disc. The outer ring beyond the black outline represents a disc that is symmetrically bulging which is very rarely seen in CT or MRI scans.
Both broad-based herniation and focal herniations are more commonly found. A total 109 patients of the lumbar disc degeneration with age group between 17 to 80 y were diagnosed studied on 15 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging machine. MRI findings like lumbar lordosis Schmorls nodes decreased disc height disc annular tear disc herniation disc bulge disc protrusion and disc extrusion were observed.
L4-L5 Posterior annular tear diffuse disc bulge with left paracentral protrusion narrowing left lateral recess with compression of left traversing nerve root. These simple words of MRI cannot tell us the severity of the pain what Mr. Dilbag Singh felt for months.
A herniated disc C6-C7 is the second most common location for a cervical herniated disc to occur. This intervertebral level lies at the base of the neck and is an area of significant disc degeneration in most people by the age of 30. C6C7 herniations are some of the most common diagnostic scapegoats for upper back neck.
A symmetrical bulging disc occurs when disc expands its borders equally in every direction. A protrusion on the other hand is when the discs border expands in one direction. If this bulge involves 25 to 50 of the discs circumference its considered a broad-based protrusion.