By strict definition a broad-based herniation involves between 25 and 50 of the disc circumference. The causes of L4-L5 bulging disc.

Unlike a herniated disc when the nucleus breaks through the annulus a bulging disc protrudes outward but the outer layers of the annulus remains intact.
Broad based annular disc bulge. A broad-based disc protrusion occurs when more than 25 percent but less than 50 percent of the disc materials circumference is extended beyond the spinal bone borders according to the American Journal of Neuroradiology. A disc is bulging when over 50 percent of the disc materials circumference is overextended. A disc has either a broad-based.
Broad based bulging discs are not any inherently worse than focal protrusions. Most broad based disc protrusions are not symptomatic or harmful in any way although some may enact pain and possible related symptoms if they affect a neurological structure. Broad based central herniated discs are often reported to impinge on the thecal sac which basically amounts to nothing.
2 Discal bulge broad based centraljright paracentral protrusion annular tear at L4-L5 with compression of thecal sac. Madhusudan Orthopaedic Surgeon Bulging disc in the neck with broad based right paracentral and foraminal disc protrusion. Broad based disc bulge is the issue of have no extra room for the persons spinal cord causing pain and numbness.
Broad based disc bulge is often thought to. In simple terms a disc bulge refers to an apparent generalized extension of disc tissues beyond the edges of the edge of vertebrae usually less than 3mm. Bulge is a term for an image and can be a normal variant usually at L5-S1.
The natural aging process causes the discs to dehydrate and lose their original form. In some cases this causes the discs to bulge. This occurs when the larger part of the disc spreads beyond its normal boundaries.
For many this common disc condition doesnt show any symptoms. Many people dont even realize they have bulging discs. If the bulge extends enough to.
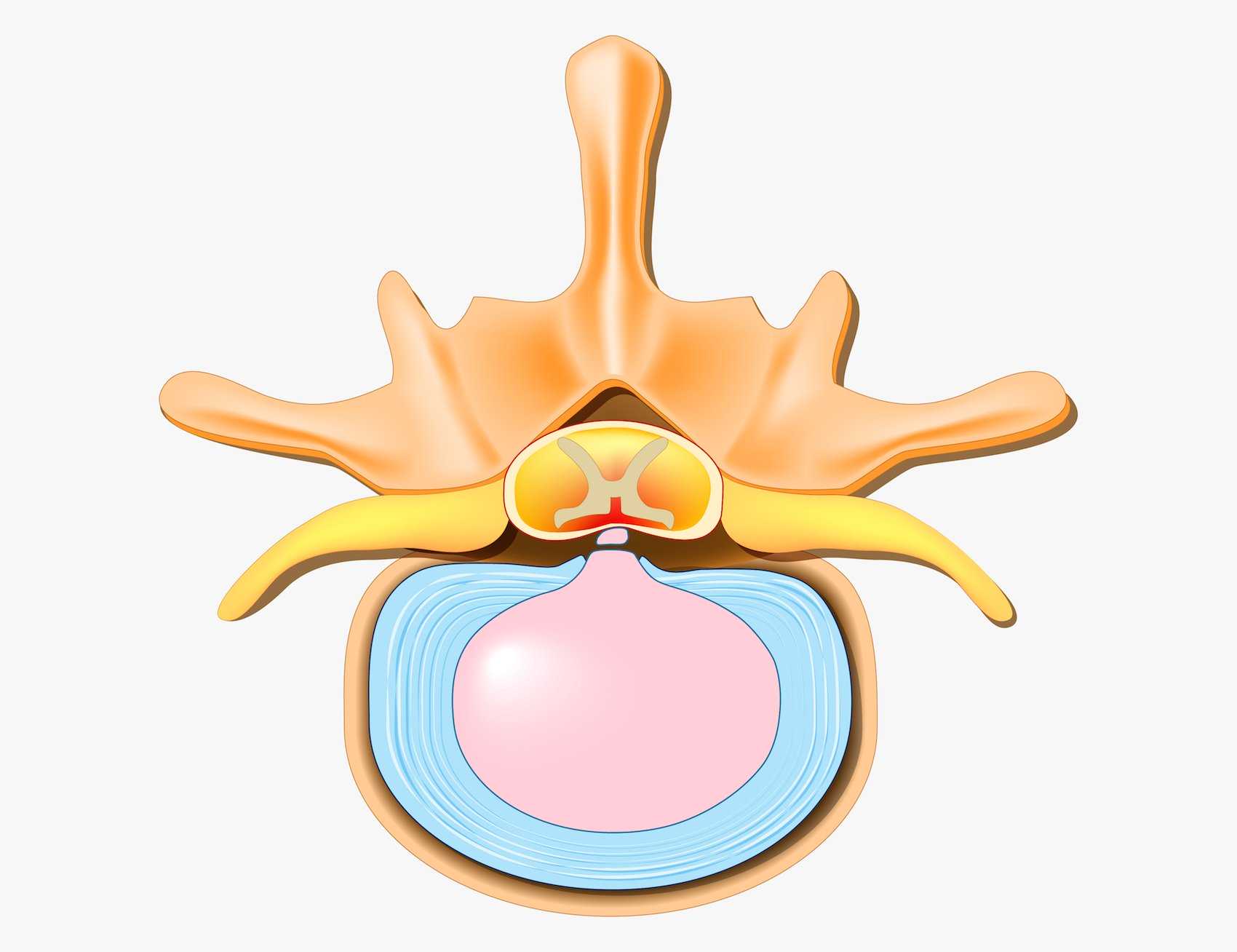
A disc bulge represents displacement of the outer fibers of the annulus fibrosus beyond the margins of the adjacent vertebral bodies involving more than one-quarter 25 or 90 degrees of the circumference of an intervertebral disc 3. Because it is limited by the annulus fibrosus it does not extend above or below the attached margins of the disc 3. Unlike a herniated disc when the nucleus breaks through the annulus a bulging disc protrudes outward but the outer layers of the annulus remains intact.
However because the disc protrudes into the spinal canal it can still compress a nerve root. Asymmetric disc bulge Broad-based disc bulge. The bulge involves 25 to 50 of the discs.
The causes of L4-L5 bulging disc. Its important to know the mechanics of your spinal column and what is happening during a disc bulge so you can embark on the proper treatment with your spine doctor. Your spine is made up of a column of bones stacked on top of each other.
Discs provide cushioning between each of these bones said Livestrong. Sometimes discs may bulge move out of place and put pressure on nerves that exit your spine. Conservative treatment that may include a combination of nerve decompression and noninvasive pain management techniques is used to treat small annular tears with disc bulges at L4 or L5 as stated by Laser Spine Institute.
The appropriate treatment for an annular tear depends largely on the cause and severity of the damaged disc. This image illustrates a typical disc bulge that is broad-based and usually does not cause nerve compression. Annular tears Small disruptions to the outer fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc known as the the annulus fibrous can occur and these are called annular tears.
Broad based left paracentral lateral protrusion of the L5S1 intervertebral disc is seen abutting the ipsilateral traversing S1 nerve. Disc bulge is seen at L4L5 with posterocentral dominancepartly effacing the ipsilateral laterak recess and mildly encroaching on the ipsilateral inferior neral foramen. Herniation was common at L4 L5 disc level 68ie.
Extrusion was common at L4 L5 disc level 18ie. Disc bulge was common at L3 L4 17ie. 2576 disc buldge L4 L5 disc level 17ie.
L3 L4 L5 S1 level shows maximum osteophytes 5ie. Mild diffuse bulge is present. No focal protrusion is seen.
Mild diffuse bulge is present. There is mild flattening of the anterior aspect of the thecal sac. There is mild narrowing of the neural foramina bilaterally.
Mild broad-based left posterolaterally disc protrusion is present. Disc bulge is a projection into spinal canal or foramina of soft gelatinous nucleus pulposus with intact fibrous annulus covering of the disc. Advertisement Lumbar foramina is a lateral bony tunnel meant to pass the spinal nerve and lumbar spinal canal accommodates lower end of spinal cord and quada equina see Figure 2.
Broad based disc protrusion is strictly defined as a disc protrusion that occurs around 25 to 50 percent of the circumference of a spinal disc. When any amount of disc material is out of place and beyond its normal boundaries it can place pressure on surrounding nerve roots causing them to relay faulty signals between the brain and other areas of the body. L5-S1 Disc Bulge Symptoms Over time the discs in the spine undergo wear and tear due to repetitive movements.
This process is absolutely normal and is a part of aging and happens with everyone. L5-S1 bulging discs are most common as they take the stress and weight of the body. The symptoms experienced in the lower back can be terribly painful.
Annular disc bulge can heal on its own eventually. Classification of Disc Bulge. Bulges in general are various and can be classified according to the circumference they involve.
Circumferential bulge is one that involves the entire circumference of the disc while asymmetric bulge is the opposite and does not involve the entire circumference. A bulging disc on the other hand can involve more than 180 degrees of the discs circumference. This means protruding discs may be viewed as potentially more serious than bulging discs because with protrusion more pressure is placed on a smaller area of the disc.
This could extend the protrusion farther into the central spinal canal or a nerve root exit. Diagnosing broad disc protrusion. You could have a protruding disc and not even realize it.
A posterior bulging disc or herniated disc occurs when a spinal disc beings to bulge. A posterior bulging disc also known as a herniated disc occurs when a spinal disc that sits between vertebrae begins to bulge due to compression. This condition can be painful.
Diagnostic image testing such as magnetic resonance imaging MRI andor a computed tomography scan CT will show a bulging disc where it is located and how severe it is. From there you can be referred to a specialist who will work with you to choose your course of treatment. Treatment for C5-C6 Disc Bulging.
Traditional Medical vs Conservative. By strict definition a broad-based herniation involves between 25 and 50 of the disc circumference. A focal herniation involves less than 25 of the disc circumference.
Herniated discs may take the form of protrusion or extrusion based on the shape of the displaced or herniated material. The following diagram illustrates this well.